
Amabile and Pratt in 2016, drawing on the literature, distinguish between creativity ("the production of novel and useful ideas by an individual or small group of individuals working together") and innovation ("the successful implementation of creative ideas within an organization"). In general, innovation is distinguished from creativity by its emphasis on the implementation of creative ideas in an economic setting. It is the means by which the entrepreneur either creates new wealth-producing resources or endows existing resources with enhanced potential for creating wealth. Innovation is the specific function of entrepreneurship, whether in an existing business, a public service institution, or a new venture started by a lone individual in the family kitchen. Specifically, innovation involves some combination of problem/opportunity identification, the introduction, adoption or modification of new ideas germane to organizational needs, the promotion of these ideas, and the practical implementation of these ideas. Workplace innovation concerns the processes applied when attempting to implement new ideas. Workplace creativity concerns the cognitive and behavioral processes applied when attempting to generate novel ideas. Organizational researchers have also distinguished innovation separately from creativity, by providing an updated definition of these two related constructs: whether it is process or product-service system innovation). whether an innovation is new to the firm, new to the market, new to the industry, or new to the world) and kind of innovation (i.e. Two main dimensions of innovation are degree of novelty (i.e. These writers define innovation as generation, admission and realization of new ideas, products, services and processes. Behn, innovation includes original invention and creative use. "An idea, practice, or object that is perceived as new by an individual or other unit of adoption" Īccording to Alan Altshuler and Robert D. It is both a process and an outcome.Īmerican sociologist Everett Rogers, defined it as follows: Innovation is production or adoption, assimilation, and exploitation of a value-added novelty in economic and social spheres renewal and enlargement of products, services, and markets development of new methods of production and the establishment of new management systems. Crossan and Apaydin built on the definition given in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Oslo Manual:
#Creator of fishbone diagram software
In a study of how the software industry considers innovation, the following definition given by Crossan and Apaydin was considered to be the most complete.
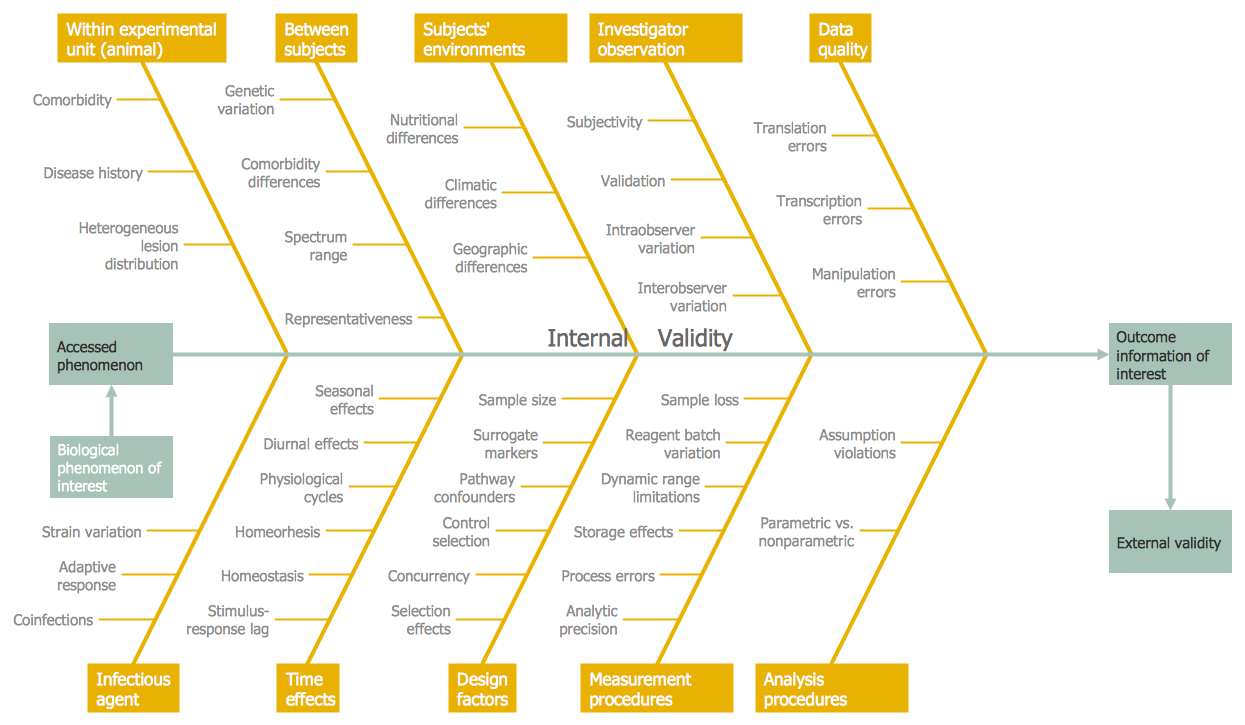
"Innovation is the multi-stage process whereby organizations transform ideas into new/improved products, service or processes, in order to advance, compete and differentiate themselves successfully in their marketplace" attempted to formulate a multidisciplinary definition and arrived at the following: found around 60 definitions in different scientific papers, while a 2014 survey found over 40. Surveys of the literature on innovation have found a variety of definitions. The opposite of innovation is exnovation. Technical innovation often manifests itself via the engineering process when the problem being solved is of a technical or scientific nature. new / improved ability) to make a meaningful impact in a market or society, and not all innovations require a new invention. Innovation is related to, but not the same as, invention: innovation is more apt to involve the practical implementation of an invention (i.e.
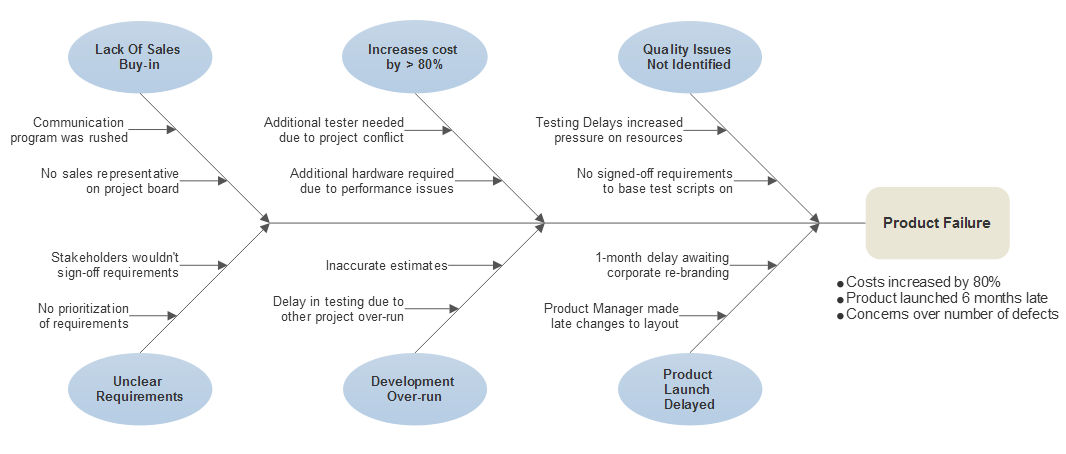
Or business models that innovators make available to markets, governments and society. Innovation often takes place through the development of more-effective products, processes, services, technologies, art works Others have different definitions a common element in the definitions is a focus on newness, improvement, and spread of ideas or technologies.
#Creator of fishbone diagram iso
ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entity realizing or redistributing value".

Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. Edison was one of the most prolific inventors in history, holding 1,093 U.S. For other uses, see Innovation (disambiguation) and Innovators (disambiguation).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
